Intelligent Automation in Healthcare

Intelligent Automation is the future, and the health industry is not immune to it. We are on the cusp of another industrial revolution that will change the way we work and interact with our patients and customers. Gartner estimates that “one-third of the workforce may be replaced by robots by the year 2025,” and that by 2018’s end, more than 3 million workers globally will be supervised by a “roboboss.” RPA and Intelligent Automation tools are being rapidly adopted by leading healthcare organizations to personalize patient experiences and interactions and automate case management functions, IT security tracking, portions of the revenue cycle, and use cases that are expanding every day.
Why is there an immediate and compelling need for RPA? Healthcare organizations are struggling to manage limited resources, and cost pressure continues to increase. The need to do things faster, better, and at lower cost is an ongoing challenge. Within healthcare, RPA can help patients, providers, and staff throughout the care continuum support pre-visit/intake processes, diagnoses, treatment, and recovery and discharge, along with supporting administrative, claims, and billing functions. The following list is not all-inclusive but shows some areas where healthcare organizations are focusing as they begin their RPA journey.
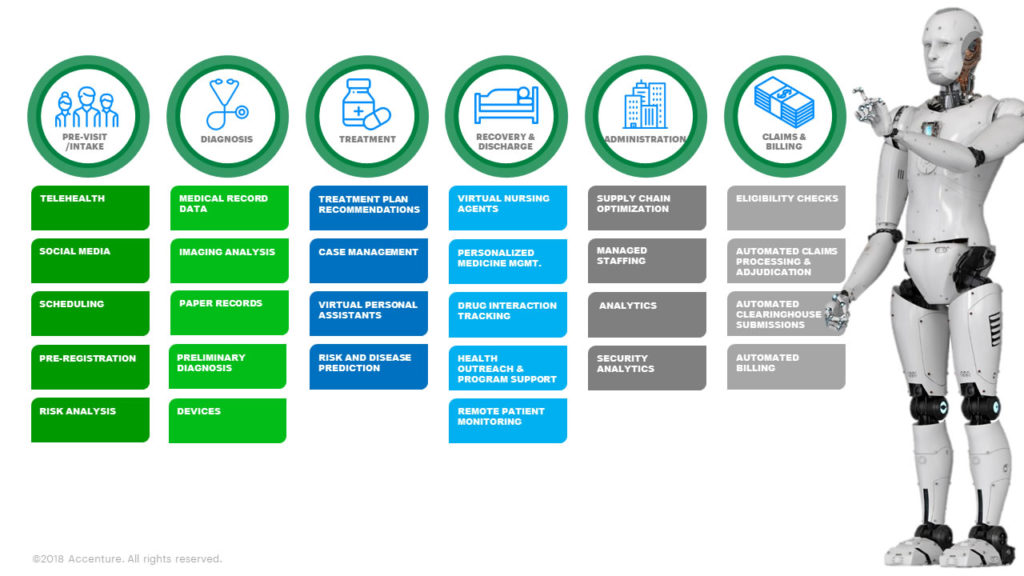
Healthcare Use Cases
A leading healthcare organization wanted to create the “Amazon of Healthcare,” where patient preferences for areas such as communication and social determinants are served up to clinicians in a timely manner. This would help professionals drive patient and clinical engagement to deliver a seamless patient experience from check-in to check-out. RPA, combined with other Intelligent Automation tools, created an intuitive experience for clinical users and minimized the duplicative data entry between the customer relationship management (CRM) system and Epic. A three-month pilot with breast cancer patients was implemented to track the tools’ impact on patient symptoms and satisfaction. The automation improved patient health outcomes and engagement, and reduced complaints, emergency department (ED) visits, and hospital readmissions.
Another healthcare organization was interested in automating key portions of its revenue cycle with a variety of payers to allow billing resources to focus on unique and complex cases rather than general data entry, including:
• Medicaid secondary billing — Calculate the fee schedule versus actual payment, submit the secondary claim, and automate contractual adjustments
• Preauthorization with commercial insurance payers — Submit imaging authorization requests through the website and transfer to staff to complete clinical components on the requests
• Professional billing cash posting — Pull bank data and allocate checks from electronic remit and handle errors for payer mismatches and separation of bundled payments
The RPA pilot is targeted to improve both the speed to completion and accuracy of the work within the revenue cycle. In both cases, the savings potential estimated by the pilot more than covered the upfront investment required to establish RPA within the organizations.
Not All Processes Are Created Equal
RPA can be a key part of your intelligent automation toolkit and is best applied after evaluating organizational processes for their suitability to RPA. For the evaluation, consider using a structured, proven methodology along four key dimensions: process effort, process overview, systems information and change pipeline.
How do you define an automation-friendly process? Generally speaking, RPA is a good match for processes with these characteristics:
• Highly manual
• High-volume
• Rule-based with limited human judgement
• Few exceptions
• Initiated by a digital trigger
• Use structured, digital data
• Use two or more systems
• Limited planned changes in process steps/rules
• High likelihood of human error
RPA, and specifically Blue Prism, in the broader Intelligent Automation context has applications in the following areas.
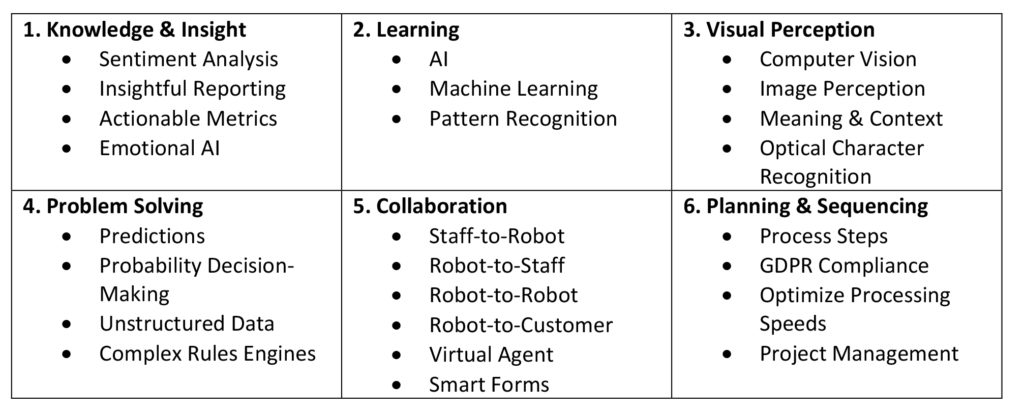
If your organization is considering an RPA journey and is not sure where to start, it is best to work with an experienced RPA implementation partner to identify and prioritize use cases that yield the highest return on investment (ROI) and demonstrate the business justification. Accenture provides an extensive use case library and proprietary tools to quickly and efficiently do exactly that.
In our next blog post, we will describe what makes a good process for RPA and potential use cases for your organization.
For more information, remember to register for the November 1 webinar “Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare.”

Accenture posts second in series of blogs in advance of Nov. 1 webinar
10/23/2018