RPA: Optimizing Healthcare, Improving Lives

Is there room for robots in the hospital? To answer that, here is a story from James MacDougall of robotic process automation (RPA) provider for Blue Prism:
“My first sortie as an Air Force pilot in an F-16 taught me one very important lesson—namely, that some technologies outstrip the human ability to maximize its performance. Since maximization is not achievable, the acceptable alternative is optimization: what to do and when to do it. How much versus how little. How fast versus how high. The human pilot must work in tandem with technology and automation to take the jet to its practical boundaries.
Healthcare is facing an opportunity for similar transformational change. Artificial intelligence (AI) and process automation on top of existing electronic medical record (EMR) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems are reducing redundant tasks and improving the access to relevant data for rapid clinical decision-making. Healthcare providers must prioritize investments and manage limited resources to optimize both patient outcomes and ongoing operations, while simultaneously minimizing risk.”
The field of AI encompasses a wide variety of tools and technologies ranging from automating routine, rules-based tasks with process automation, to creating digital and virtual assistants and creating self-learning models powered by machine learning and cognitive computing. As a first step, providers are beginning to use RPA to automate redundant tasks, provide rapid access to clinical data and recommendations, and realize improved workforce satisfaction and return on investment (ROI).
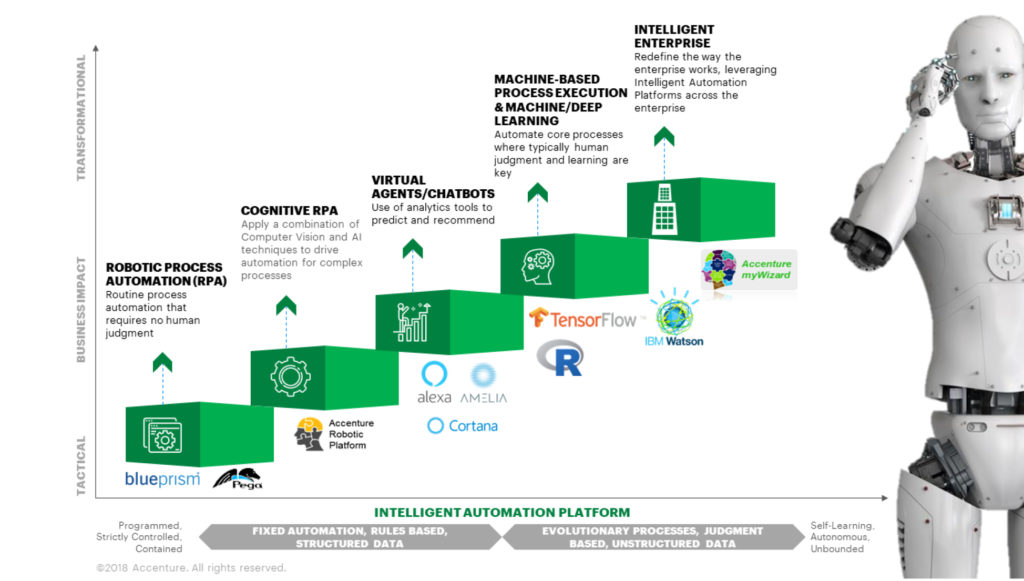
Types of Robotic Process Automation
With RPA, provider health organizations can systemically improve the lives of patients, employees, and related third parties. This three-part blog series explains how.
For starters, there are three types of process automation solutions:
1. Recorded Desktop Automation (RDA): Records and replays individual, tactical tasks that usually involve navigating systems on a desktop.
2. Software Development Kits (SDKs): Target IT users rather than business users and are best suited for organizations working on custom IT integration projects or who want to retain full control of the process automation capability within the IT function.
These two categories solve for narrow needs, whether simple automation of a few routine tasks or a major IT integration undertaking. But neither adequately addresses unique enterprise-level concerns. The only solution designed with the security and technology needs of the whole organization in mind is the third category—the RPA Digital Workforce.
3. RPA Digital Workforce: Provides capabilities for automating processes that would ordinarily be manually performed by humans or through extensive customization of existing IT systems. It is a centrally managed, scalable, and server-based digital workforce that meets the needs of both operations and IT to deliver strategic benefit across the company. To support enterprise-worthiness and data security, IT governs the digital worker like any human employee, but the business operations typically manage configuration, control, and monitoring of the RPA “robots” (i.e., run-time resources).
Successfully implementing, managing, and scaling an RPA environment of digital workers requires a commitment from the healthcare organization. Managing the implementation and use of RPA is like any transformational, organizational project, with consideration for the implications of process selection, prioritization, standard IT-related processes and controls, and effective project and change management. The use of RPA requires a cultural acceptance within the organization to effectively incorporate the digital worker and realize optimal ROI. It also demands experience and industry expertise from an RPA integrator that understands how RPA fits into the organization’s broader ecosystem of Intelligent Automation and solves for its strategic business objectives.
Consider the possibilities of an RPA journey done well. What would be the benefits of automating or even partially automating some of the most copious or complex processes in your healthcare organization?
RPA delivers significant ROI by compressing the revenue cycle, taking costs and risks out of the business, and delivering massive hours back to it. And patients, for whom you are ultimately in business, are served faster, receive more facetime with practitioners, enjoy accurate billing and faster payer reimbursement, and are far more likely to be satisfied.
Watch out for our next blog post, where we will describe what makes a good process for RPA and potential use cases for your organization. For more information, remember to register for the November 1 webinar “Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare.”

Accenture posts first of series of blogs in advance of Nov. 1 “RPA” webinar
10/18/2018